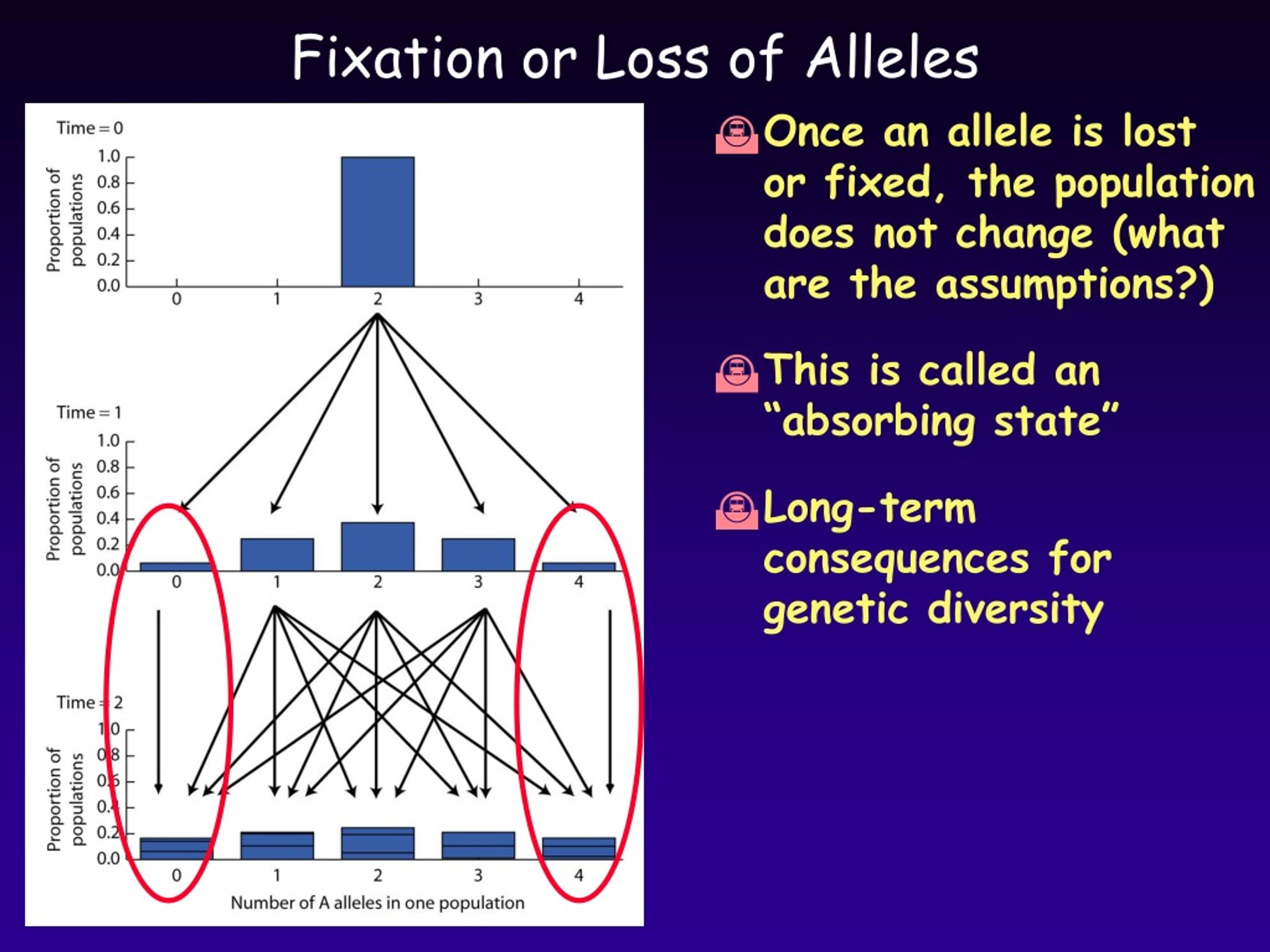
Webin this tutorial, we’ll see how a small population size can lead allele frequencies within a population to randomly change. This change is called genetic drift. Genetic drift is a. Web — with these examples, you now have a better idea of what genetic drift is, how it works in the real world and what type of impact genetic drift can have on a. Web — it is true that genetic drift contributes to evolution or the gradual modification of a population's gene pool. However, random changes, not selection forces. Webgenetic drift occurs when the frequency of alleles in a population changes by random chance. Among the given options, a massive storm that randomly kills many individuals. Web — unlike natural selection, genetic drift describes the effect of chance on populations in the absence of positive or negative selection pressure. Web — genetic drift, also known as allelic drift or the wright effect, refers to the random change in the allele frequency of a particular gene in a population. It is one of. Web — genetic drift can be defined as the loss of alleles from a population by chance. It is one of the four elements that influence the evolution of a gene pool, along. Web — genetic drift is defined as the changing of the number of available alleles in a population by chance events. Also called allelic drift, this phenomenon is usually due. Web — genetic drift example. In the below example, the frequency of the brown and white butterflies is eight and two in generation i respectively. Web — one example of genetic drift is the founder effect, where a small group of individuals establishes a new population with a limited genetic diversity due to the small. Genetic drift is a mechanism of evolution that causes random changes in the frequency of alleles (versions of a gene) in a population over time. Webunder a scenario of pure genetic drift, the probability of fixation of an allele in a population is its initial frequency in the population. If the initial frequency of an allele is 0. 01, then. Genetic drift vs gene flow. Genetic drift is an evolutionary change in allelic frequencies of a population as a matter of chance. Web — in genetic drift, alleles change frequency within a population due to random sampling. As a result, it does not produce adaptations. Two mechanisms cause genetic. Webgenetic drift describes random fluctuations in the numbers of gene variants in a population. Genetic drift takes place when the occurrence of variant forms of a gene,. Web — on the one hand, colorado’s plan could provide a buffer population, a reservoir of about 100 wolverines, to create an even more diverse genetic pool as other.