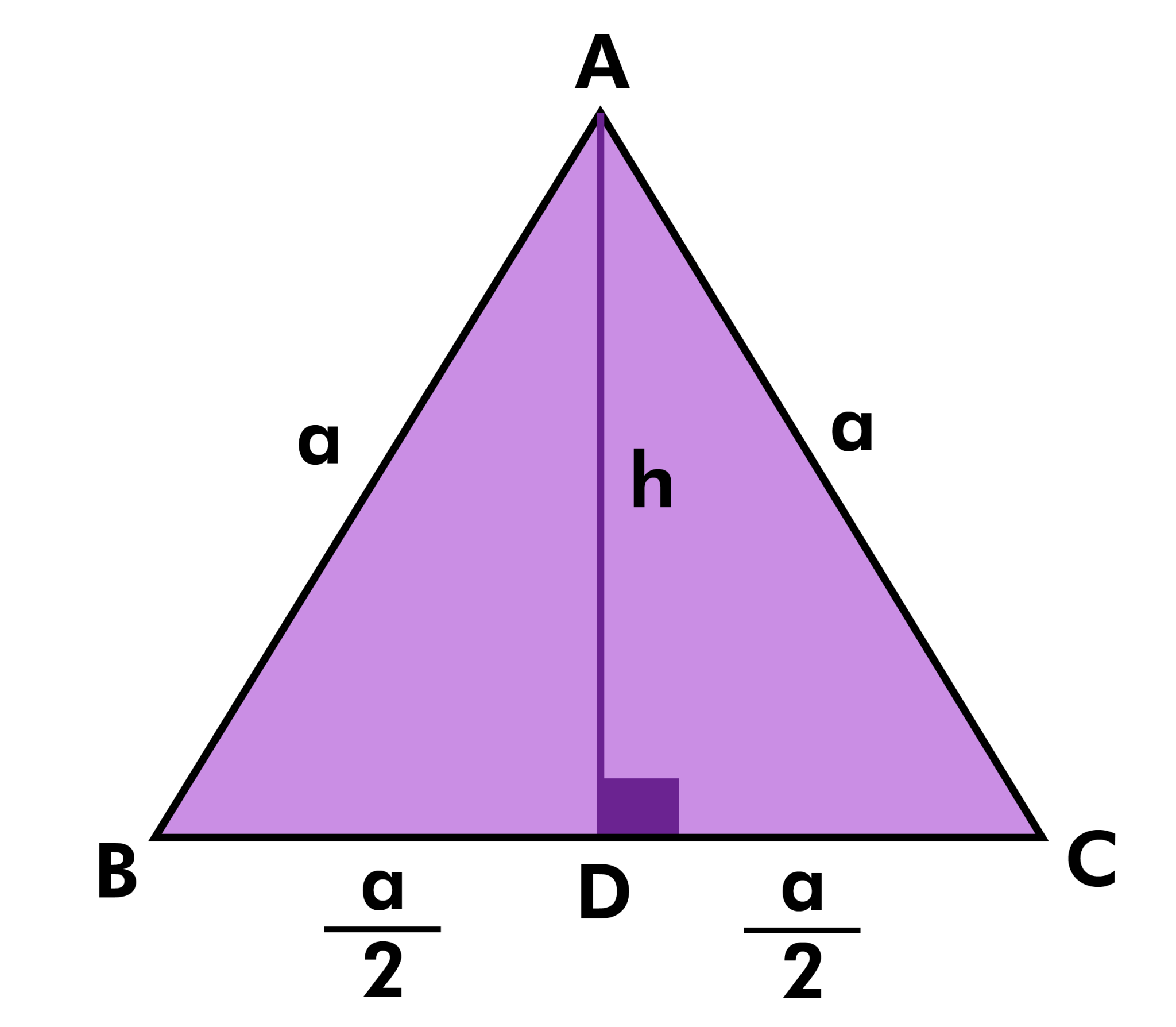
— an equilateral triangle is a triangle with all sides equal and all angles equal to 60 degrees. The area of an equilateral triangle depends on the length of its sides and can be. The area of an equilateral triangle is basically the amount of space occupied by an equilateral triangle. In an equilateral triangle, the median, angle bisector and perpendicular are all the. If all the sides are equal in length, then such triangles are called an equilateral triangle. Now, if we consider the triangles based on the interior angles, they are again classified into three. The triangle inequality theorem states that: A < b + c, b < a + c, c < a + b. In any triangle, the shortest distance from any vertex to the opposite side is the perpendicular. In figure below, xp. Given an equilateral triangle inscribed on a circle and a point on the circle. The distance from the point to the most distant vertex of the triangle is the sum of the distances from the point to the. Viviani's theorem, named after vincenzo viviani, states that the sum of the shortest distances from any interior point to the sides of an equilateral triangle equals the length of the triangle's. If abc is an equilateral triangle and p is a point on the arc bc of the circumcircle of the triangle abc, then; Pa = pb + pc. For a cyclic quadrilateral. The basic formula for triangle area is side a (base) times the height h, divided by 2: Area = (a × h) / 2. Height of the equilateral triangle is derived. — an equilateral triangle is a special case of a triangle where all 3 sides have equal length and all 3 angles are equal to 60 degrees. The altitude shown h is h b or, the altitude of. If three sides of a triangle are equal and the measure of all three angles is equal to 60 degrees then the triangle is an equilateral triangle. The distance formula can be used to. Ptolemy's theorem gives a relationship between the side lengths and the diagonals of a cyclic quadrilateral; It is the equality case of ptolemy's inequality. Pompeiu's theorem is a result of plane geometry, discovered by the romanian mathematician dimitrie pompeiu. The theorem is simple, but not classical. The equilateral triangle theorem states that if a triangle is equiangular, then the triangle is also equilateral. An image below shows a triangle. See full answer below. An equilateral triangle is a triangle with all three sides equal in length. According to the angle bisector theorem, the angle bisector of a triangle divides the opposite side into two parts that are proportional to the other two sides of the triangle. — learn about the equilateral triangle, a regular polygon with all sides and angles equal to 60 degrees. Find out the formulas for area, perimeter, height, centroid and circumcenter, and the equilateral triangle theorem. The height of an equilateral triangle can be determined by using the pythagorean theorem. First, draw a perpendicular line from one vertex to the base of the triangle. This line is called the height. In plane geometry, morley's trisector theorem states that in any triangle, the three points of intersection of the adjacent angle trisectors form an equilateral triangle, called the first morley.