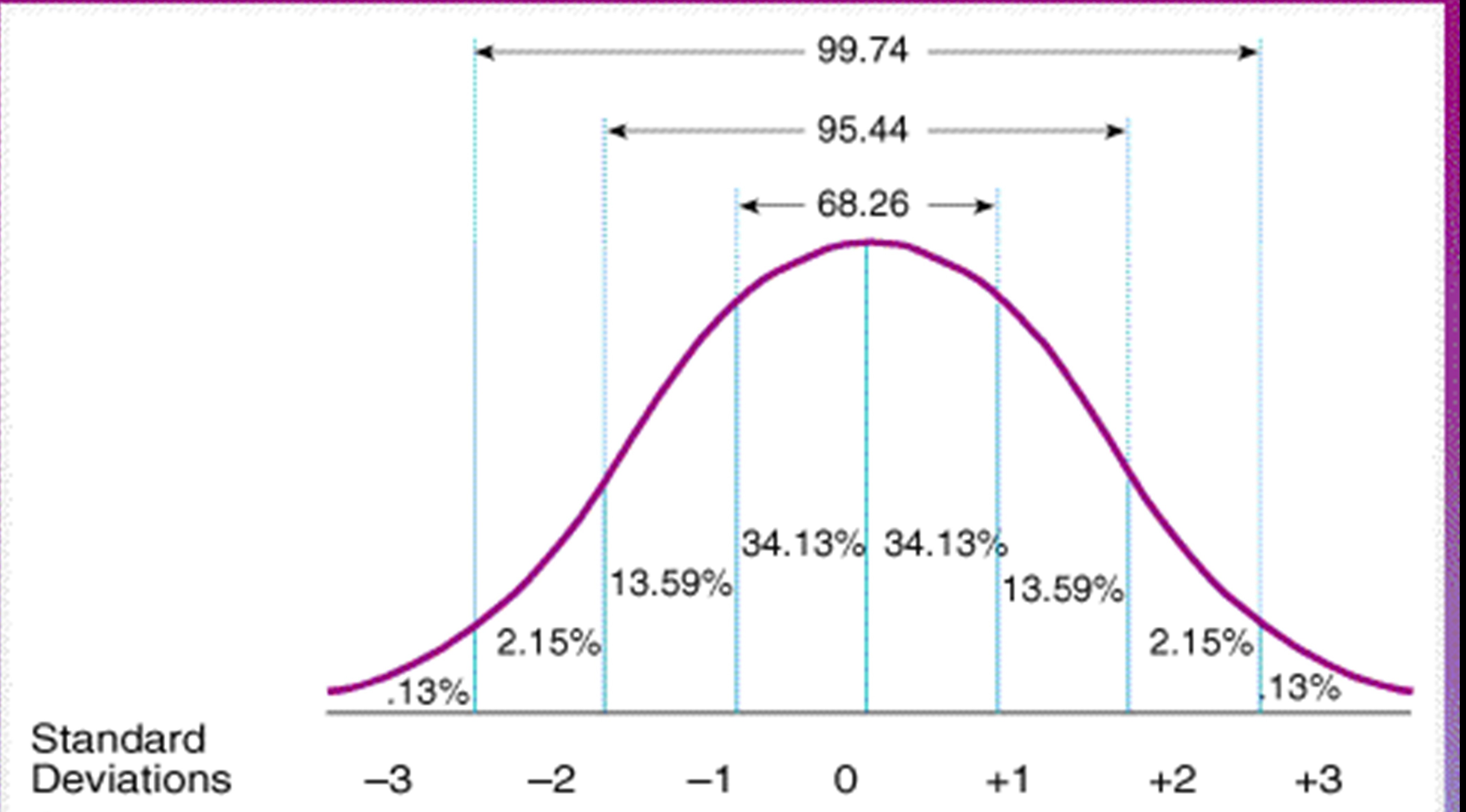
The standard deviation measures how concentrated the data are around the mean; The more concentrated, the smaller the standard deviation. A small standard deviation can. The standard deviation has the same unit as the variable, and will scale with them when you change units. The correlation coefficient, on the other hand, is unitless. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *. kastatic. org and *. kasandbox. org are unblocked. But the variance is a squared measure and does not have the same units as the data. No one knows what 9. 7375 years squared means. Taking the square root solves the. The standard deviation is expressed in the same units as the mean is, whereas the variance is expressed in squared units, but for looking at a distribution, you can use either just so long as. You and your friends have just measured the heights of your dogs (in millimeters): The heights (at the shoulders) are: 600mm, 470mm, 170mm, 430mm and 300mm. Put simply, the standard deviation is the average distance from the mean value of all values in a set of data. 1,000 people were questioned about their monthly phone. Standard deviation is a measure which shows how much variation (such as spread, dispersion, spread,) from the mean exists. The standard deviation indicates a “typical” deviation from. Find out what are the units of variance and standard deviation. Get to know better quartiles, percentiles, quantiles, standard deviation and variance. Standard deviation is a statistical measurement that looks at how far individual points in a dataset are dispersed from the mean of that set. If data points are further from the. By marco taboga, phd. Standard deviation is a measure of how much the realizations of a random variable are dispersed around its mean. The deviations are used to calculate the standard deviation. If the numbers belong to a population, in symbols a deviation is x − μ. For sample data, in symbols a deviation is x − ˉx. The standard deviation is in the same units as your data. For example, if you measure age in years, the standard deviation is also in years, which is one reason that people use the. This makes it hard to interpret and visualize. Standard deviation, on the other hand, is in the same units as the original data. In the next section we will describe a different measure of dispersion, the standard deviation, which has the same units as the data. The standard deviation determines the spread of the distribution, that is, the amount of variation relative to the center. More specifically, it determines the average distance of the observations.