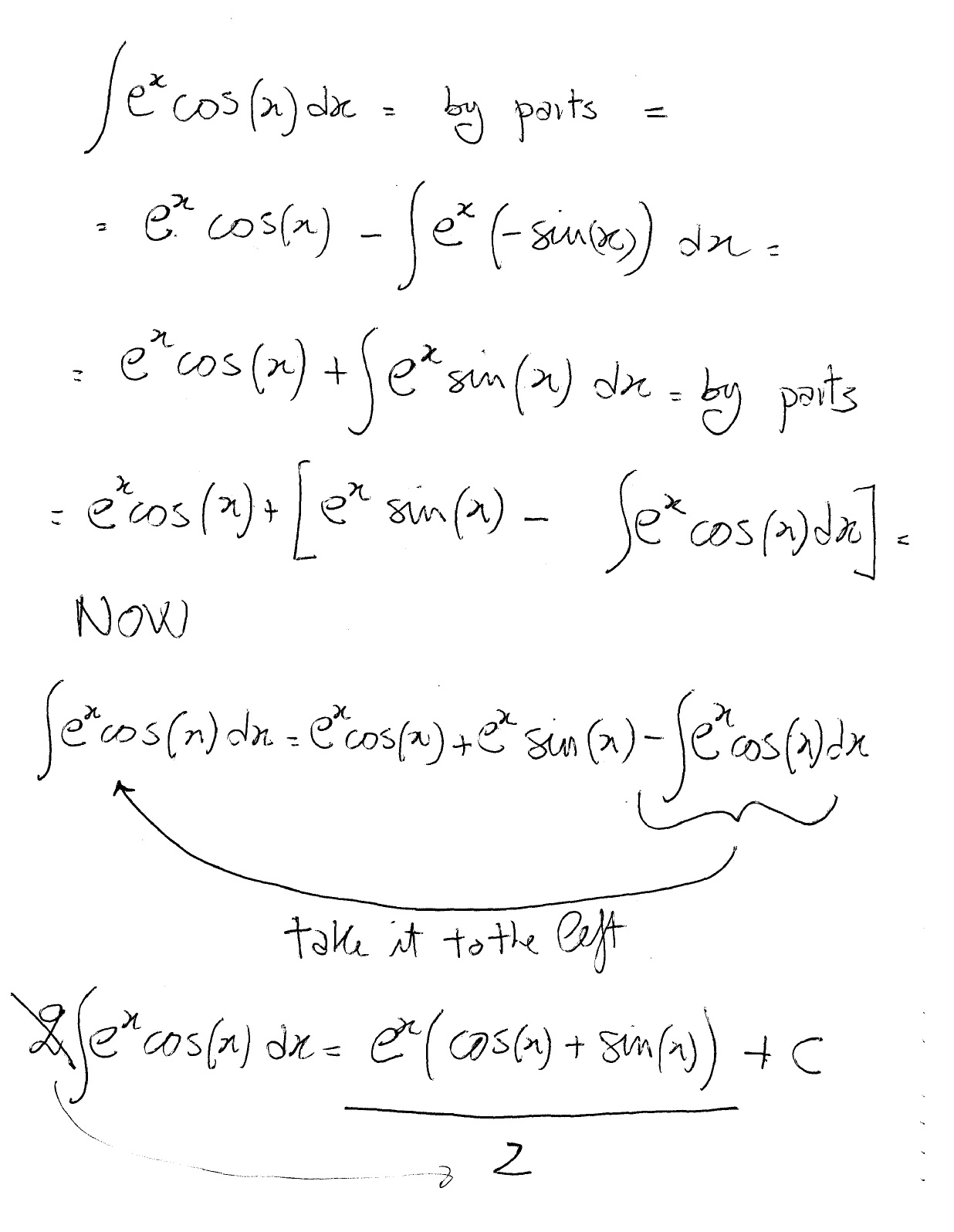Solving simultaneous equations is one small algebra step further on from simple equations. Extended keyboard examples upload random. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase,. The answer is the antiderivative of the function f (x) = e2x f (x) = e 2 x. F (x) = f (x) = 1 2e2x +c 1 2 e 2 x + c. Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry,. Type in any integral to get the solution, steps and graph Example 4. 1. 4 antiderivative of \(\sin x, \cos 2x\) and \(\frac{1}{1+4x^2}\). Consider the functions \begin{align*} f(x) &= \sin x + \cos 2x & g(x) &= \frac{1}{1+4x^2}. Continued fraction identities containing integrals; Series of int x/e^2 dx; Furthermore, \(\dfrac{x^2}{2}\) and \(e^x\) are antiderivatives of \(x\) and \(e^x\), respectively, and the sum of the antiderivatives is an antiderivative of the sum. Antiderivative of e^(2x) natural language; Extended keyboard examples upload random. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase,. Let's start by finding the antiderivative: \[ \int e^x\, dx=e^x+c \nonumber \] so we know that \( f(x)=e^x+\text{(some constant)} \), now we just need to find which one. U = − 2x ⇒ du dx = −2. Y = eu ⇒ dy du = eu. By the chain rule we have: Dy dx = dy du × du dx. Dy dx = eu × − 2e−2x = −2e−2x. Now integration is the reverse of. The calculator will instantly provide the solution to your calculus problem, saving you time and effort. The antiderivative of #e^(2x)# is equivalent to #=inte^(2x)dx# let #u=2x#, so #du=2dx#. Here, we can make some substitutions: The antiderivative of #e^(2x)# is a function whose derivative is #e^(2x)#. But we know some things about derivatives at this point of the course. Among other things, we know. We answer the first part of this question by defining antiderivatives. The antiderivative of a function f f is a function with a derivative f. Why are we interested in antiderivatives? Type in any equation to get the solution, steps and graph Consider the function \(f(x)=2x\). Knowing the power rule of differentiation, we conclude that \(f(x)=x^2\) is an antiderivative of \(f\) since \(f′(x)=2x\). Are there any other. Consider the function \(f(x)=2x\). Knowing the power rule of differentiation, we conclude that \(f(x)=x^2\) is an antiderivative of \(f\) since \(f′(x)=2x\). Are there any other. Determining the antiderivative of e 2 x. The antiderivative of e 2 x is the function of x whose derivative is e 2 x we know that, d d x (e 2 x) = 2 e 2 x · d x. Rearranging the terms we get. Wolfram|alpha is a great tool for calculating antiderivatives and definite integrals, double and triple integrals, and improper integrals. The wolfram|alpha integral calculator also shows. \int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n} show more